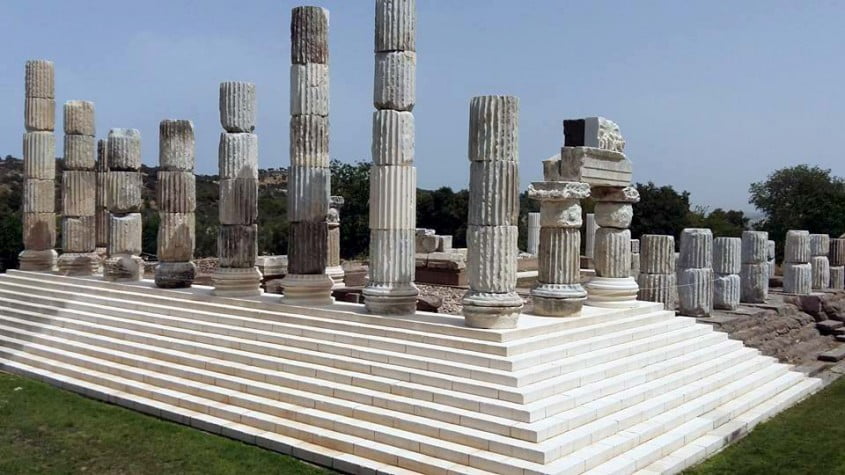
The Sanctuary of Apollo Smintheion (Temenos), located in Gülpınar Town of Çanakkale’s Ayvacık district, is the sanctuary where God Apollo was honored with the epitheton of Smintheus. The Sanctuary of Smintheus is also mentioned in the Iliad Epic.

This is one of the most important sanctuaries of the Hellenistic period. Smintheion sanctuary was one of the important cult centers of Troas in ancient times.
Location of Apollon Smintheus Sanctuary
The Sanctuary of Apollon Smintheus is located in the southwest corner of the Biga Peninsula of Canakkale Province. This sanctuary is located within the borders of Gülpınar town of Ayvacık district of Çanakkale.
This Temple is located on the hillside of the valley between the northwest and the northeast of the Gülpınar Town. It was founded in today’s Bahceli region, which is rich in water. Apollon sanctuaries are usually located near water sources or directly at the source, such as Smintheus sanctuary. The reason for this is that the priests who foretold the future in the name of God prophesied by looking at the water.
Cult of Smintheus
“Sminthos” is the name given to the mouse in the ancient Mysia language. The mouse is the holy animal of god Apollo. Therefore, the cult of Smintheus is closely related to mice. In the birth of the cult of Apollo, the damage and disasters caused by the mice have a big share. God Apollo established justice by punishing the powerful kings for their injustice to their people, by plague epidemics spreading with mice.

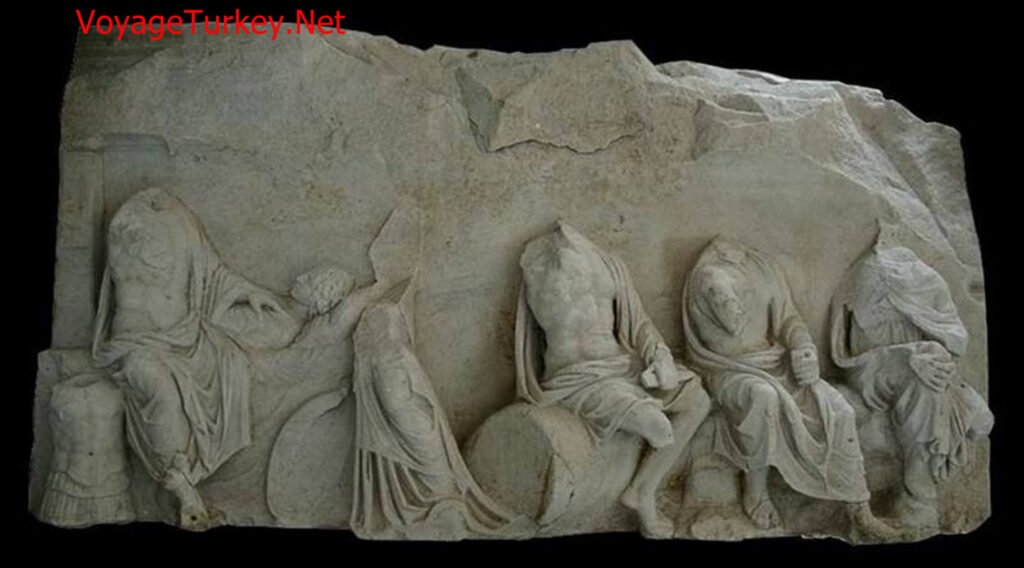
According to Homer’s Iliad epic, the Greek army to Troia plundered the cities along the way and kidnapped women and girls. Agamemnon, the king of Akha, headed by the Greek army, stopped by Chrysa (today’s Gülpınar) and kidnaps the daughter of the priest of the temple of Apollo Smintheus. The priest, who is trying hard to get his daughter back, calls on his God Apollo and asks him to bring his daughter back. Angry Apollo infects the Greek army with the plague epidemic through mice. The Greek army breaks through the plague and has to give her back. The priest’s daughter is brought to Chrysa under the supervision of Odysseus. In gratitude, the god Apollon was sacrificed in the temple.
Buildings in Sanctuary of Apollon Smintheus
In the excavations carried out in the Sanctuary of Apollo Smintheus; a prehistoric settlement, the Temple of Apollo Smintheus, 7 water reservoirs belonging to the Roman period, 2 large Roman baths serving those who come to the temple to worship, 7 water cisterns with different capacity that provide water to these baths, and the sacred road were unearthed. You can see these structures on the map below.
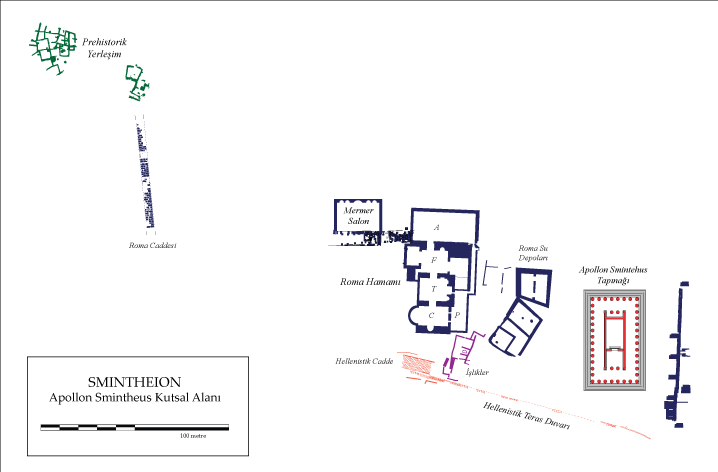
Temple of Apollo Smintheus
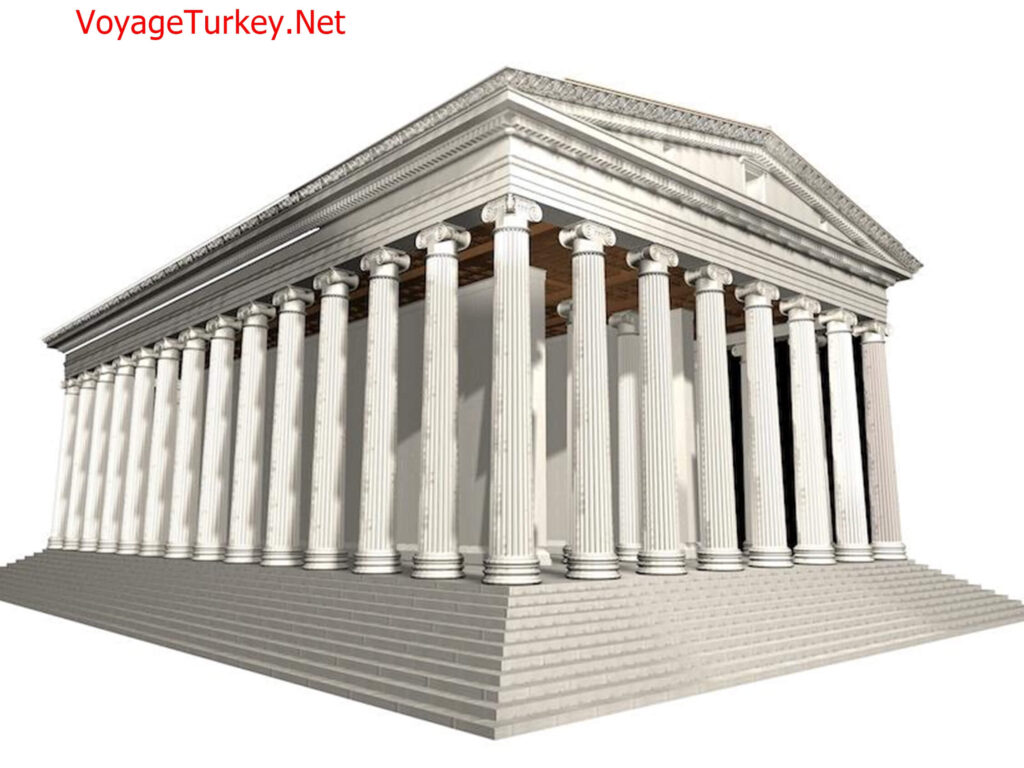
The largest and most basic structure in the sanctuary is this temple. The temple is one of the most important structures exhibiting ancient Greek architecture and sculpture. It is surrounded by a total of 44 marble columns, 8 on short sides and 14 on long sides. The mythological scenes of the Iliad epic were first described in detail in the column reliefs (friezes) on the upper part of this temple.
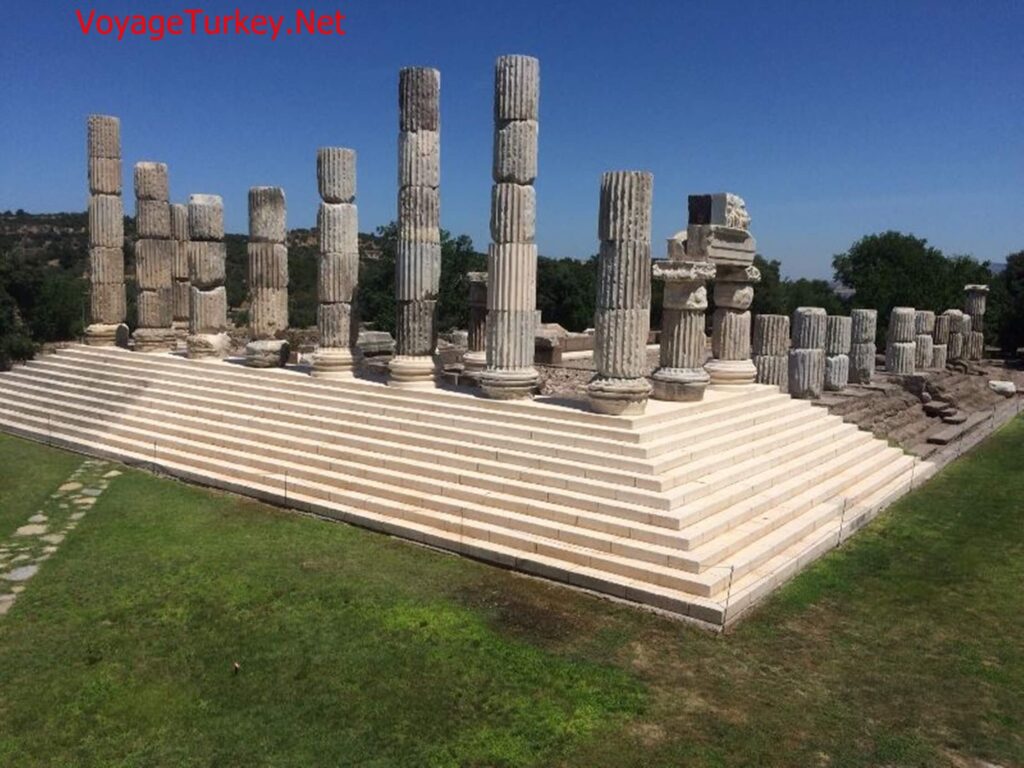

The Temple of Apollo Sminteus in this area was built in the 2nd century BC.
This temple collects the theme of the Hellenistic period with its architectural design and style
Sacred Way
The sacred road connects the Sanctuary of Apollo Smintheus to the town of Alexandria Troas, 35 kilometers north.
Water Cisterns
There are 7 water cisterns in the sanctuary that provide water for the baths. The capacity of each cistern is different.
The number of cisterns in the Sacred Area is quite high due to the difficulty of transporting water from a distance, the amount of rainfall falling in the region, and the dry summer months.
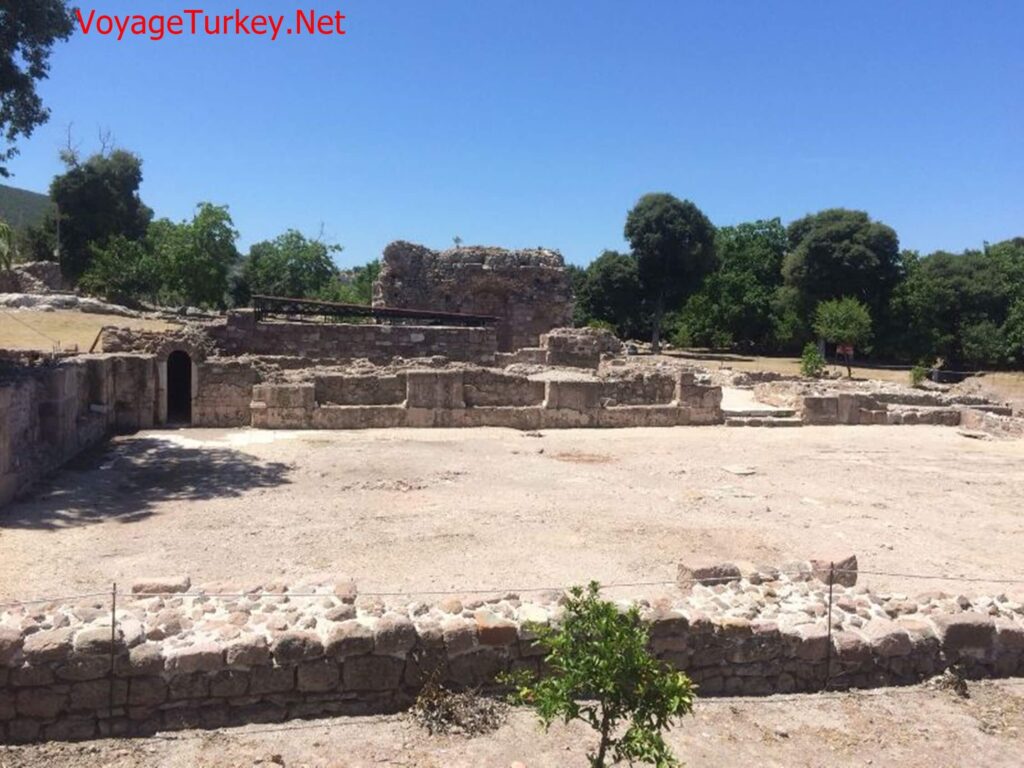

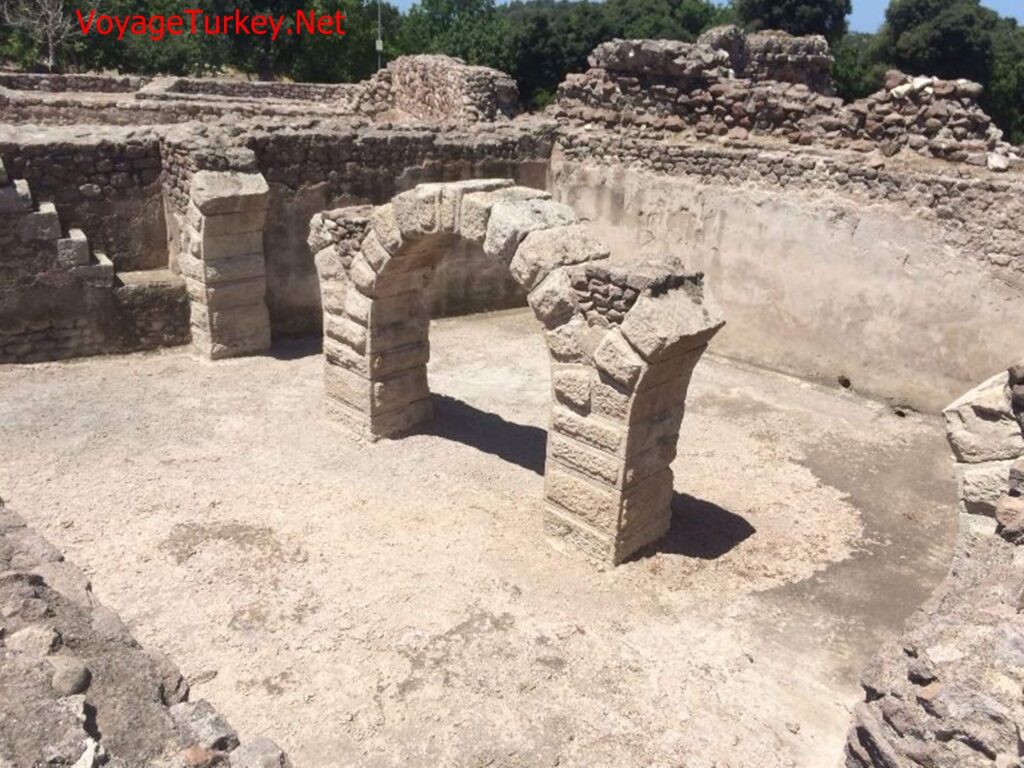
Roman Baths
2 baths were built for the guests who came to the sanctuary to be washed and cleaned before worship. The Hamas are dated to the Roman Empire.

Sports Games Area
The sports games area is located to the west of the baths. In the sports field, the statues of the athletes who were awarded in the sports competitions organized in the name of God Apollo were erected. The statues on the marble bases are probably bronze and have not survived to the present day.